Question 1 Topic 5, Case Study 5Case Study Question View Case
Based on the PaaS prototype, which Azure SQL Database compute tier should you use?
- A. Business Critical 4-vCore
- B. Hyperscale
- C. General Purpose v-vCore
- D. Serverless
Answer:
A
Explanation:
There are CPU and Data I/O spikes for the PaaS prototype. Business Critical 4-vCore is needed.
Incorrect Answers:
B: Hyperscale is for large databases
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/reserved-capacity-overview
Comments
Question 2 Topic 5, Case Study 5Case Study Question View Case
Which audit log destination should you use to meet the monitoring requirements?
- A. Azure Storage
- B. Azure Event Hubs
- C. Azure Log Analytics
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Scenario: Use a single dashboard to review security and audit data for all the PaaS databases.
With dashboards can bring together operational data that is most important to IT across all your Azure resources, including
telemetry from Azure Log Analytics.
Note: Auditing for Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics tracks database events and writes them to an audit log
in your Azure storage account, Log Analytics workspace, or Event Hubs.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/visualize/tutorial-logs-dashboards
Comments
Question 3 Topic 6, Case Study 6Case Study Question View Case
Which windowing function should you use to perform the streaming aggregation of the sales data?
- A. Sliding
- B. Hopping
- C. Session
- D. Tumbling
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Scenario: The sales data, including the documents in JSON format, must be gathered as it arrives and analyzed online by
using Azure Stream Analytics. The analytics process will perform aggregations that must be done continuously, without
gaps, and without overlapping.
Tumbling window functions are used to segment a data stream into distinct time segments and perform a function against
them, such as the example below. The key differentiators of a Tumbling window are that they repeat, do not overlap, and an
event cannot belong to more than one tumbling window.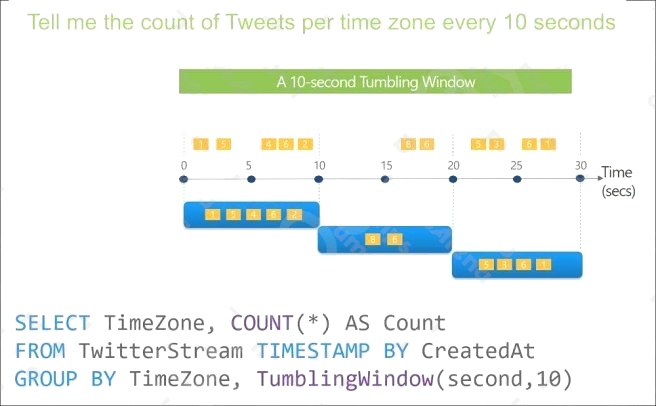
Reference: https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/azure-docs/blob/master/articles/stream-analytics/stream-analytics-window-
functions.md
Comments
Question 4 Topic 6, Case Study 6Case Study Question View Case
Which counter should you monitor for real-time processing to meet the technical requirements?
- A. SU% Utilization
- B. CPU% utilization
- C. Concurrent users
- D. Data Conversion Errors
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Scenario: Real-time processing must be monitored to ensure that workloads are sized properly based on actual usage
patterns.
To monitor the performance of a database in Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance, start by monitoring
the CPU and IO resources used by your workload relative to the level of database performance you chose in selecting a
particular service tier and performance level.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/monitor-tune-overview
Comments
Question 5 Topic 7, Case Study 7Case Study Question View Case
You need to provide an implementation plan to configure data retention for ResearchDB1. The solution must meet the
security and compliance requirements.
What should you include in the plan?
- A. Configure the Deleted databases settings for ResearchSrv01.
- B. Deploy and configure an Azure Backup server.
- C. Configure the Advanced Data Security settings for ResearchDB1.
- D. Configure the Manage Backups settings for ResearchSrv01.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/long-term-backup-retention-configure
Comments
Question 6 Topic 7, Case Study 7Case Study Question View Case
HOTSPOT
You need to recommend a configuration for ManufacturingSQLDb1 after the migration to Azure. The solution must meet the
business requirements.
What should you include in the recommendation? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: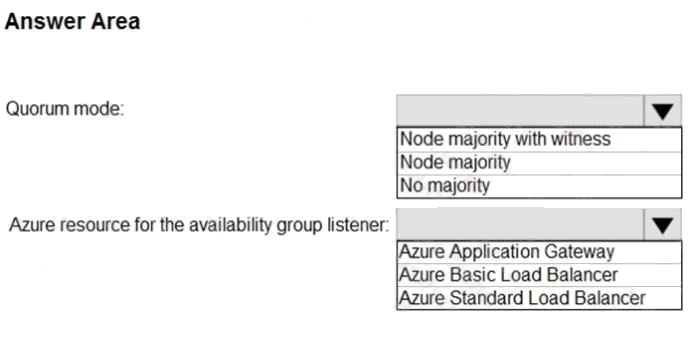
Answer:
Explanation:
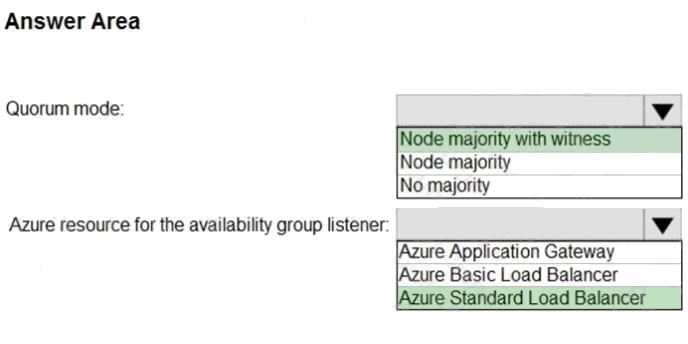
Box 1: Node majority with witness
As a general rule when you configure a quorum, the voting elements in the cluster should be an odd number. Therefore, if
the cluster contains an even number of voting nodes, you should configure a disk witness or a file share witness.
Note: Mode: Node majority with witness (disk or file share)
Nodes have votes. In addition, a quorum witness has a vote. The cluster quorum is the majority of voting nodes in the active
cluster membership plus a witness vote. A quorum witness can be a designated disk witness or a designated file share
witness.
Box 2: Azure Standard Load Balancer
Microsoft guarantees that a Load Balanced Endpoint using Azure Standard Load Balancer, serving two or more Healthy
Virtual Machine Instances, will be available 99.99% of the time.
Scenario: Business Requirements
Litware identifies business requirements include: meet an SLA of 99.99% availability for all Azure deployments.
Incorrect Aswers:
Basic Balancer: No SLA is provided for Basic Load Balancer.
Note: There are two main options for setting up your listener: external (public) or internal. The external (public) listener uses
an internet facing load balancer and is associated with a public Virtual IP (VIP) that is accessible over the internet. An
internal listener uses an internal load balancer and only supports clients within the same Virtual Network.
Reference:
https://technet.microsoft.com/windows-server-docs/failover-clustering/deploy-cloud-witness https://azure.microsoft.com/en-
us/support/legal/sla/load-balancer/v1_0/
Comments
Question 7 Topic 7, Case Study 7Case Study Question View Case
What should you do after a failover of SalesSQLDb1 to ensure that the database remains accessible to SalesSQLDb1App1?
- A. Configure SalesSQLDb1 as writable.
- B. Update the connection strings of SalesSQLDb1App1.
- C. Update the firewall rules of SalesSQLDb1.
- D. Update the users in SalesSQLDb1.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Scenario: SalesSQLDb1 uses database firewall rules and contained database users.
Comments
Question 8 Topic 8, Mixed Questions
What should you use to migrate the PostgreSQL database?
- A. Azure Data Box
- B. AzCopy
- C. Azure Database Migration Service
- D. Azure Site Recovery
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/dms/dms-overview
Comments
Question 9 Topic 8, Mixed Questions
You have 20 Azure SQL databases provisioned by using the vCore purchasing model.
You plan to create an Azure SQL Database elastic pool and add the 20 databases.
Which three metrics should you use to size the elastic pool to meet the demands of your workload? Each correct answer
presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A. total size of all the databases
- B. geo-replication support
- C. number of concurrently peaking databases * peak CPU utilization per database
- D. maximum number of concurrent sessions for all the databases
- E. total number of databases * average CPU utilization per database
Answer:
A C E
Explanation:
CE: Estimate the vCores needed for the pool as follows:
For vCore-based purchasing model: MAX(,
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/elastic-pool-overview
Comments
Question 10 Topic 8, Mixed Questions
DRAG DROP
You have SQL Server 2019 on an Azure virtual machine that contains an SSISDB database.
A recent failure causes the master database to be lost.
You discover that all Microsoft SQL Server integration Services (SSIS) packages fail to run on the virtual machine.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence to resolve the issue? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the
list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct.
Select and Place: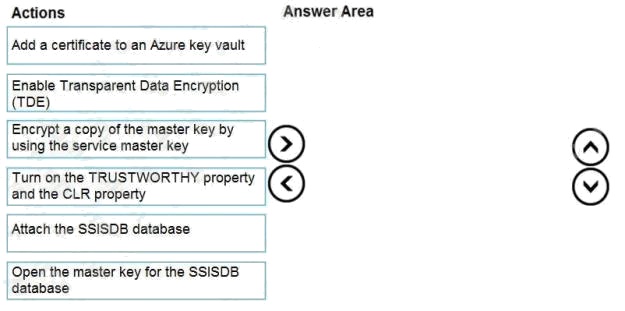
Answer:
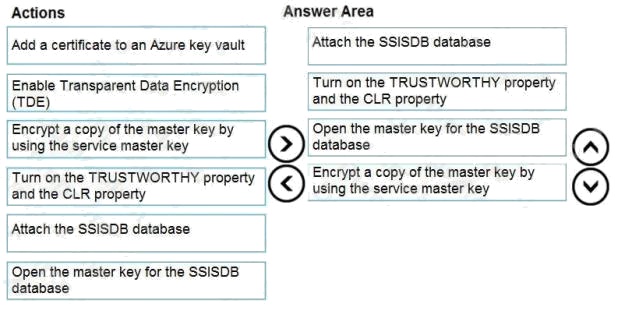
Explanation:
Step 1: Attach the SSISDB database
Step 2: Turn on the TRUSTWORTHY property and the CLR property
If you are restoring the SSISDB database to an SQL Server instance where the SSISDB catalog was never created, enable
common language runtime
(clr)
Step 3: Open the master key for the SSISDB database
Restore the master key by this method if you have the original password that was used to create SSISDB.
open master key decryption by password = 'LS1Setup!' --'Password used when creating SSISDB' Alter Master Key Add
encryption by Service Master Key
Step 4: Encrypt a copy of the mater key by using the service master key
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/integration-services/backup-restore-and-move-the-ssis-catalog
Implement a Secure Environment
Comments
Page 1 out of 19
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 197
page 2