oracle 1z0-821 practice test
Solaris 11 System Administration Exam
Last exam update: Apr 14 ,2025
Question 1
View the Exhibit to inspect the boot environment Information displayed within a non global zone on
your system.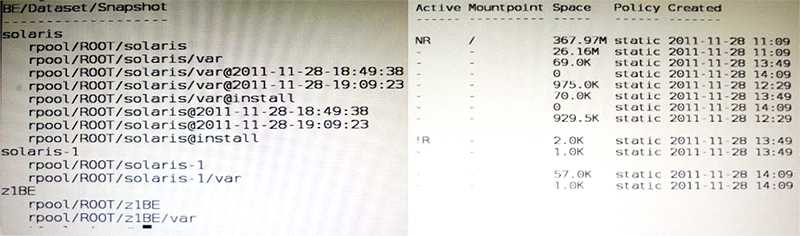
Which two options describe the solaris-1 boot environment?
- A. The solaris-1 boot environment is not bootable.
- B. The solaris-1 boot environment is incomplete.
- C. The solaris-1 boot environment was created automatically when the non global zone was created.
- D. The solaris-1 boot environment was created in the non-global zone using the beadm create command.
- E. The solaris-1 boot environment is associated with a non active global zone boot environment.
Answer:
A,E
Explanation:
A: The of the Active Column indicates that this boot environment is inactive, and hence not
bootable.
Note: The values for the Active column are as follows:
R Active on reboot.
N Active now.
NR Active now and active on reboot.
- Inactive.
! Unbootable boot environments in a non-global zone are represented by an exclamation point.
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23824_01/html/E21801/unbootable.html#scrolltoc
Question 2
The COMSTAR framework provides support for the iSCSI protocol.
Select three options that correctly describe the COMSTAR framework.
- A. iSCSI devices can be used as dump devices.
- B. SCSI commands are carried over IP networks and enable you to mount disk devices from across the network onto your local system.
- C. Large amounts of data can be transferred over an IP network with very little network degradation.
- D. COMSTAR allows you to convert any Solaris11 host into a SCSI target device that can be accessed over a storage network.
- E. One IP port can handle multiple ISCSI target devices.
Answer:
B,D,E
Explanation:
B: By carrying SCSI commands over IP networks, the iSCSI protocol enables you to access block
devices from across the network as if they were connected to the local system. COMSTAR provides
an easier way to manage these iSCSI target devices.
D: Common Multiprotocol SCSI TARget, or COMSTAR, a software framework that enables you to
convert any Oracle Solaris 11 host into a SCSI target device that can be accessed over a storage
network by initiator hosts.
E: One IP port can handle multiple iSCSI target devices.
Question 3
Your task is to convert a JumpStart sysidcfg file to an Automated Installer (AI) sc_profile.xml file,
using js2ai.
Select two unsupported items that will require changes.
- A. terminal = zterms
- B. name_service-NTS+
- C. timezone=US/pacific
- D. system_locale=en_US
- E. network_interface=PRIMARY
- F. root_password=rJmvLUXM10cU
Answer:
A,D
Explanation:
A: terminal
The js2ai tool does not perform any translation. Make sure the terminal type speciied in the sysidcfg
ile is supported in Oracle Solaris 11.
D: system_locale
The js2ai tool does not perform any translation. Make sure the locale specified in the sysidcfg ile is
supported in Oracle Solaris 11.
Question 4
A change in your companys security policy now requires an audit trial of all administrators assuming
the sysadm role, capturing:
There are two command necessary to accomplish this change. One is a rolemod command. What is
the other?
- A. auditconfig set policy=argv
- B. auditconfig -setpolicy +argv
- C. auditconfig -setflags lo, ex sysadm
- D. auditconfig set flags=lo, ex sysadm
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Audit Significant Events in Addition to Login/Logout (see step 2 below)
Use this procedure to audit administrative commands, attempts to invade the system, and other
significant events as specified by your site security policy.
For all users and roles, add the AUE_PFEXEC audit event to their preselection mask.
# usermod -K audit_flags=lo, ps:no username
# rolemod -K audit_flags=lo, ps:no rolename
# auditconfig -setpolicy +argv
3- Record the environment in which audited commands are executed.
# auditconfig -setpolicy +arge
Note: [-t] -setpolicy [+|-]policy_flag[, policy_flag ...]
Set the kernel audit policy. A policy policy_flag is literal strings that denotes an audit policy. A prefix
of + adds the policies specified to the current audit policies. A prefix of - removes the policies
specified from the current audit policies. No policies can be set from a local zone unless the perzone
policy is first set from the global zone.
Question 5
You are creating a non-global zone on your system.
Which option assigns a zpool to a non-global zone, and gives the zone administrator permission to
create zfs file system in that zpool?
- A. While creating the non-global zone, make the following entry: add deviceset match=/dev/rdsk/c4t0d0endBoot the zone and log in the zone as root. Create the zpool: zpool create pool2 c4t0d0In the non-global zone, root can now create ZFS file system in the pool2 zpool
- B. In the global zone, create the zpool: global# zpool create pool2 c4t1d0While creating the no-global zone, make the following entry: add datasetset name=pool2endadd fsset dir=pool1set special=pool1set type=zfspool1endBoot the zone, log in the zone as root, and create the zfs file system in the pool2 zpool.
- C. In the global zone, create the zpool:global#zpool create pool2 c4t1d0While creating the global zone, make the following entry: add datasetset name=pool2endBoot the zone, log in to the zone as root and create the zfs file systems in the pool2 zpool.
- D. In the global zone, create the zpool and the ZFS file systems that you want to use in the non-global zone: global#zpool create pool2 c4t1d0global#zfs create pool2/dataWhile creating the non-global zone, make the following entry for each ZFS file system that you want to make available in the zone: add fsset dir=/dataset special=pool2/dataset type=zfsend
- E. Create the zpool in the global zone: global#zpool create pool2 c4t1d0Boot the non-global zone, log in to the zone as root, and issue this command to delegate ZFS permissions to root: non-global zone# zfs allow root create , destroy, mount pool2Log in to the non-global zone create ZFS file systems in the pool2 zpool.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19253-01/819-5461/gbbst/index.html
Question 6
The current ZFS configuration on server is: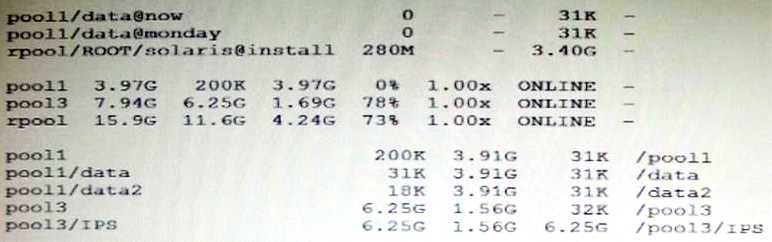
You need to backup the /data file system while the file system is active.
Select the option that creates a full backup of the /data file system and stores the backup on server in
the pool named backup.
- A. Mount -F nfs system: /backup / mntzfs snapshot pool/data@monday>/mnt/Monday
- B. Mount -F nfs systemB: /backup/mntzfs snapshot pool1/data@Mondayzfs clone pool1/data@monday/mnt/Monday
- C. Zfs send pool1/data@Monday | ssh system zfs recv backup/monday
- D. Zfs snapshot pool1/data@Monday | ssh system zfs recv backup/monday
Answer:
C
Explanation:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23823_01/html/819-5461/ghzvz.html
Question 7
You created a new zpool. Now you need to migrate the existing ZFS file system from pool1/prod to
pool2/prod.
You have these requirements:
1. Users must have access to the data during the migration, so you cannot shutdown the file system
while the migration takes place.
2. Because you want to copy the data as quickly as possible, you need to increase the server
resources devoted to the ZFS migration.
Which method would you use to modify the ZFS shadow migration daemon defaults to increase the
concurrency and overall speed of migration?
- A. Svccfg - s filesystem/shadowd:defaultsetprop config_params/shadow_threads=integer: 16endsvcadm refresh filesystem/shadowd: default
- B. Specify the -b <blocksize> option with the zfs create command and increase the value of <blocksize>
- C. Use the -o -volblocksize=<blocksize>option with the zfs create command and increase the value of the default <blocksize>.
- D. Svccfg -s filesystem/zfs: defaultsetprop config_params/shadow_threads = integer: 16endsvcadm refresh filesystem/zfs:default
Answer:
A
Explanation:
shadowd is a daemon that provides background worker threads to migrate data for a shadow
migration. A shadow migration gradually moves data from a source file system into a new shadow
file system. Users can access and change their data within the shadow file system while migration is
occurring.
The shadowd service is managed by the service management facility, smf(5). Administrative actions
on this service, such as enabling, disabling, or requesting restart, can be performed using
svcadm(1M). The service's status can be queried using the svcs(1) command.
The svccfg(1M) command can be used to manage the following parameter related to shadowd:
config_params/shadow_threads
Note: Oracle Solaris 11: In this release, you can migrate data from an old file system to a new file
system while simultaneously allowing access and modification of the new file system during the
migration process.
Setting the shadow property on a new ZFS file system triggers the migration of the older data. The
shadow property can be set to migrate data from the local system or a remote system with either of
the following values:
file:///path
nfs://host:path
Question 8
You are troubleshooting the Oracle Solaris11 Automated Installer (AI), which is not connecting with
the IPS software repository.
Which three steps will help determine the cause of DNS name resolution failure?
- A. Verify the contents of /etc/resolve.conf.
- B. Run netstat -nr to verify the routing to the DNS server.
- C. Ping the IP address of the IPS server to verify connectivity.
- D. On the installation server, verify that the menu.1st file for the client points to a valid boot arc hive.
- E. Run df -k to verify that the boot directory containing the boot archive is loopback mounted under /etc/netboot.
- F. Run the command /sbin/dhcpinfo DNSserv to ensure that the DHCP server providing the DNS server information.
Answer:
A,B,F
Explanation:
Check DNS
* (A) Check whether DNS is configured on your client by verifying that a non-empty /etc/resolv.conf
file exists.
* (F) If /etc/resolv.conf does not exist or is empty, check that your DHCP server is providing DNS
server information to the client:
# /sbin/dhcpinfo DNSserv
If this command returns nothing, the DHCP server is not set up to provide DNS server information to
the client. Contact your DHCP administrator to correct this problem.
* (B) If an /etc/resolv.conf file exists and is properly configured, check for the following possible
problems and contact your system administrator for resolution:
** The DNS server might not be resolving your IPS repository server name.
** No default route to reach the DNS server exists.
Question 9
New features wore added to ZFS in Oracle Solaris11. Your justification to upgrade from Solaris10 to
oracle Solaris11 is that it will be possible to take advantage of the enhancements that were made to
ZFS.
Identify the three ZFS functions and features that are included in Oracle Solaris 11, but not in Solaris
10.
- A. Encrypted ZFS datasets
- B. Ability for ZFS to detect and remove redundant data from the tile system
- C. Shadow Data Migration
- D. Ability to split a mirrored ZFS storage pool
- E. Ability to use ZFS on the boot drive and boot to a ZFS root file system.
- F. elimination of the swap file system when using ZFS on the root disk
Answer:
A,B,C
Explanation:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/solaris11/overview/solaris-matrix-1549264.html
Question 10
You are setting up a local IPS package repository on your Oracle Solaris11 server:
solaris.example.com.
You want to point the existing local IPS publisher to the new local IPS repository located in /repo.
These are the stops that you have followed:
1. Download and rsync the contents of the Oracle Solaris11 repository ISO image to the /repo
directory.
2. Configure the repository server service properties. The svcprop command display, the IPS related
properties:
pkg/inst_root astring/repo
pkg/readonly Boolean true
The 1s command displays the contents of the /repo directory:
#ls/repo
Pkg5.repository publisher
The svcs publisher command shows the svc: /application/pkg/server: default service is online.
The pkg publisher command shows the svc: /application/pkg/server: default service is online.
The pkg publisher command still displays:
PUBLISHERTYPESTATUSURI
solarisoriginonlinehttp://pkg.oracle.com/solaris/release/
Which steps needs to be performed to set the local IPS publisher to the local IPS repository/repo?
- A. Issue the pkgrepo refresh -s command to refresh the repository.
- B. Restart the svc:/application/pkg/server:default service.
- C. pkg set-publisher command to set the new repository location.
- D. Issue the pkgrepo rebuild command to rebuild the repository.
- E. Issue the pkgrepo set command to set the new repository location.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Set the Publisher Origin To the File Repository URI
To enable client systems to get packages from your local file repository, you need to reset the origin
for the solaris publisher. Execute the following command on each client:
Example:
# pkg set-publisher -G '*' -M '*' -g /net/host1/export/repoSolaris11/ solaris
Question 11
United States of America export laws include restrictions on cryptography.
Identify the two methods with which these restrictions are accommodated in the Oracle Solaris 11
Cryptographic Framework.
- A. Corporations must utilize signed X.509 v3 certificates.
- B. A third-party provider object must be signed with a certificate issued by Oracle.
- C. Loadable kernel software modules must register using the Cryptographic Framework SPI.
- D. Third-party providers must utilize X.509 v3 certificates signed by trusted Root Certification Authorities.
- E. Systems destined for embargoed countries utilize loadable kernel software modules that restrict encryption to 64 bit keys.
Answer:
B,C
Explanation:
B: Binary Signatures for Third-Party Software
The elfsign command provides a means to sign providers to be used with the Oracle Solaris
Cryptographic Framework. Typically, this command is run by the developer of a provider.
The elfsign command has subcommands to request a certificate from Sun and to sign binaries.
Another subcommand verifies the signature. Unsigned binaries cannot be used by the Oracle Solaris
Cryptographic Framework. To sign one or more providers requires the certificate from Sun and the
private key that was used to request the certificate.
C: Export law in the United States requires that the use of open cryptographic interfaces be
restricted. The Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework satisfies the current law by requiring that
kernel cryptographic providers and PKCS #11 cryptographic providers be signed.
Question 12
View the Exhibit and review the zpool and ZFS configuration information from your system.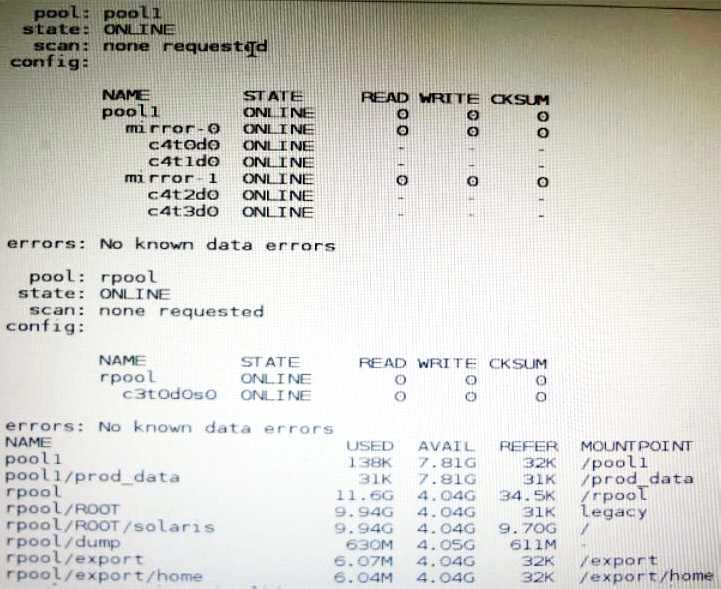
Identify the correct procedure for breaking the /prod_data mirror, removing c4t0d0 and c4t2d0, and
making the data on c4t0d0and c4t2d0 accessible under the dev_data mount point.
- A. zpool split pool1 pool2 c4t0d0 c4t2d0zpool import pool2zfs set mountpoint = /dev_data pool2/prod_data
- B. zpool detach pool1 pool2zpool attach pool2zfs set mountpoint=/dev_data pool2/prod_data
- C. zpool split pool1/prod_data -n pool2/dev_datazfs set mountpoint = /dev_data pool2/prod_data
- D. zpool split pool1 pool2 c4t0d0 c4t2d0zpool import pool2
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In this Solaris release, you can use thezpool splitcommand to split a mirrored storage pool, which
detaches a disk or disks in the original mirrored pool to create another identical pool.
After the split operation, import the new pool.
Question 13
You need to set up a local package repository to serve 75 client systems. Multiple clients will being
the package repository concurrently and you need to ensure that the local repository performs very
well under this heavy load, especially during package intensive operations.
Which option would ensure the best performance of the repository during package-intensive rations
by multiple clients?
- A. Set up multipathing on the package repository server to distribute the network load multiple network interfaces.
- B. Deploy a second instance of the package repository server to run as a read writable mirror.
- C. Deploy a second instance of the package repository server to run as a read-only mirror.
- D. Deploy a second instance of the package repository server to run as a clone of the primary repository server.
- E. Deploy a package repository locally on each client.
Answer:
A
Question 14
You run the command dlstat show-link -r.
Select the two correct statements regarding the information displayed in the INTRS column.
- A. No value is listed for virtual network interfaces.
- B. A value of 0 is listed for virtual interfaces and ether stubs.
- C. The number of Interrupts is listed, which indicates network efficiency.
- D. A number equal to the number of transmitted Ethernet frames is listed for physical links.
- E. The number of packets that were interrupted by a collision is listed, which may indicate hardware problems.
Answer:
C,E
Explanation:
In this output, the statistics for interrupt (INTRS) are significant. Low interrupt numbers indicate
greater efficiency in performance. If the interrupt numbers are high, then you might need to add
more resources to the specific link.
Example:
# dlstat -r -i 1
LINK IPKTS RBYTES INTRS POLLS CH<10 CH10-50 CH>50
e1000g0 101.91K 32.86M 87.56K 14.35K 3.70K 205 5
nxge1 9.61M 14.47G 5.79M 3.82M 379.98K 85.66K 1.64K
vnic1 8 336 0 0 0 0 0
e1000g0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
nxge1 82.13K 123.69M 50.00K 32.13K 3.17K 724 24
vnic1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Note: dlstat show-link [-r [-F] | -t] [-i interval] [-a] [-p] [ -o field[, ...]] [-u R|K|M|G|T|P] [link]
Display statistics for a link.
-r
Display receive-side statistics only. Includes bytes and packets received, hardware and software
drops, and so forth.
List of supported RX fields:
link
iusedby
ibytes
ipkts
intrs
polls
hdrops: hardware drops
sdrops: software drops (owing to bandwidth enforcement)
ch<10: number of packet chains of length < 10
ch10-50: number of packet chains of length between 10 and 50
ch>50: number of packet chains of length > 50
Question 15
Identify three options that describe the new Oracle Solaris 11 zone features.
- A. There are boot environments for zones.
- B. Administrators can delegate common administration tasks by using RBAC.
- C. Oracle Solaris 11 supports Solaris 8, 9, and 10 branded zones.
- D. You can migrate a physical Solaris 10 system and its non-global zones to a solaris10 branded zone running on an Oracle Solaris 11 system.
- E. It is possible to change the host ID of a zone.
Answer:
A,B,D
Explanation:
A: The beadm utility includes support for creating and administering non-global zone boot
environments.
Note: A boot environment is a bootable instance of the Oracle Solaris operating system image plus
any other application software packages installed into that image. System administrators can
maintain multiple boot environments on their systems, and each boot environment can have
different software versions installed.
B: Role-based access control (RBAC) is a security feature for controlling user access to tasks that
would normally be restricted to the root role. By applying security attributes to processes and to
users, RBAC can divide up superuser capabilities among several administrators.